A shift in global weather patterns may be on the horizon as the cooling influence of La Niña weakens. Experts are observing signs that could lead to the development of El Niño later this summer, a phenomenon known to bring significant climatic changes, including potential droughts and increased rainfall in different parts of the world. This potential transition carries substantial implications for agriculture, water resources, and the frequency of extreme weather events globally.
Shifting Climate Dynamics
The Earth's weather system is currently in a transition phase. For a considerable period, the La Niña pattern, characterized by cooler-than-average sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific Ocean, has been influencing global weather. However, recent updates indicate that La Niña is expected to fade in the coming weeks.
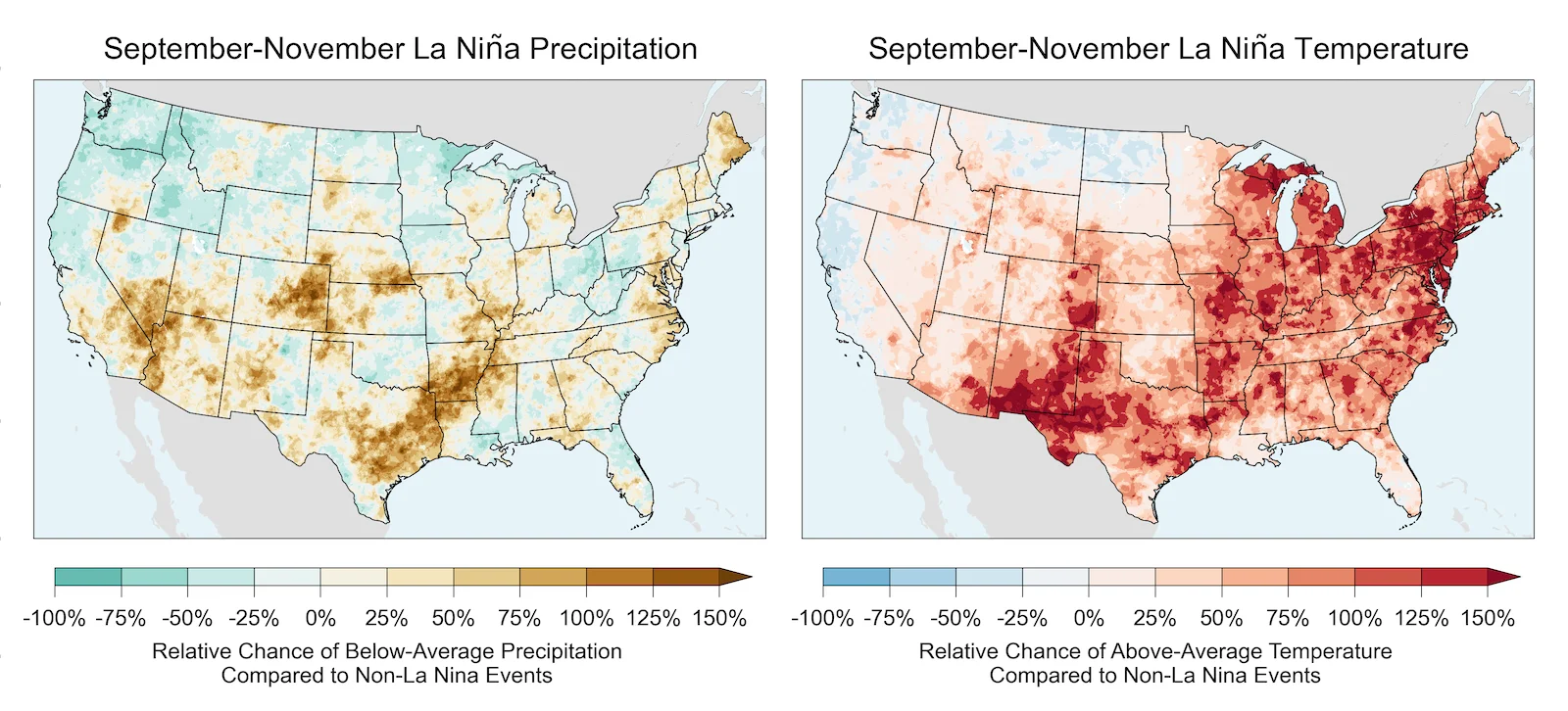
La Niña's Influence: This pattern has been subtly guiding weather conditions worldwide since last autumn.
Neutral Conditions: Following La Niña, the tropical Pacific is expected to enter a neutral state. During these periods, neither El Niño nor La Niña dictates global weather, allowing other factors to exert stronger regional influences.
El Niño's Potential Emergence: Scientists are now watching for the development of El Niño, a phenomenon marked by warmer-than-average sea surface temperatures in the same Pacific region.
Measuring the Climate Shift
The El Niño-Southern Oscillation (ENSO), which encompasses both El Niño and La Niña, is a critical climate driver. Its shifts can alter weather patterns across continents.
Read More: Winter Storm Warning for Southern Ontario: Snow, Ice Expected
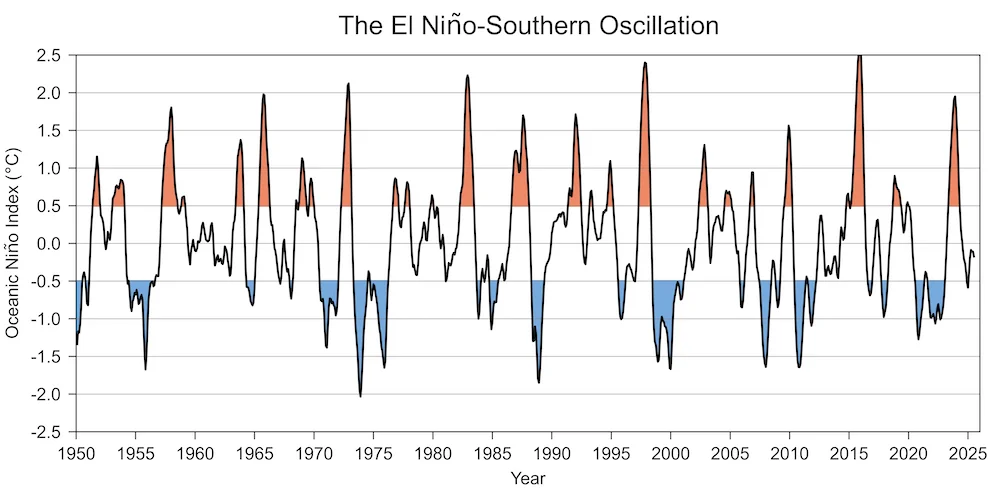
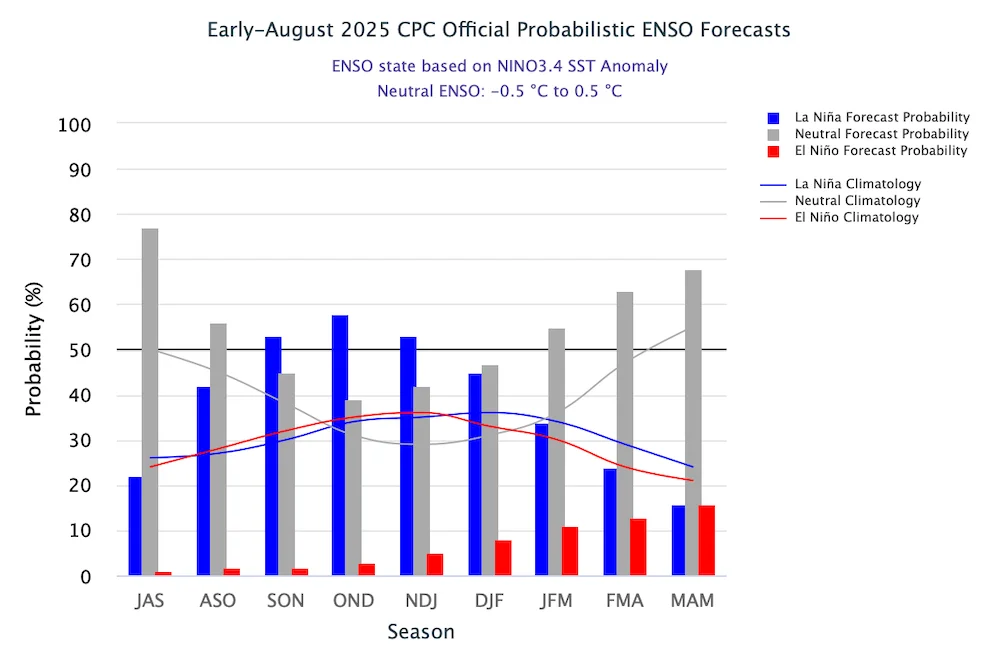
Oceanic Niño Index (ONI): This is the primary tool used by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Association (NOAA) to track and predict ENSO events. An El Niño is officially declared when sea surface temperatures in the eastern Pacific near the equator are at least 0.5 degrees Celsius above average for five overlapping three-month periods.
Impact on Precipitation: El Niño events are known to reduce the likelihood of below-average precipitation and above-average temperatures in the southern United States during autumn, winter, and spring. Conversely, La Niña can alter these chances, affecting drought conditions.
Historical Context and Observed Impacts
El Niño and La Niña cycles have a demonstrable history of influencing weather.
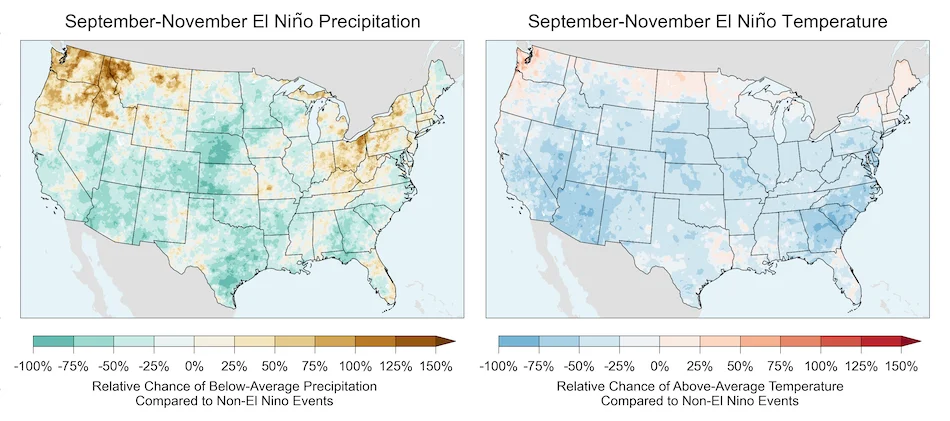
Previous El Niño: An El Niño event that was underway in June 2023 was associated with record-breaking global average ocean temperatures. This period also raised concerns about increased risks of floods, droughts, wildfires, and potential economic costs.
Recent Neutrality: As of early June 2024, El Niño has ended, and the tropical Pacific is in a neutral state. Neither El Niño nor La Niña conditions are expected in the immediate six months following this period.
Potential Effects of El Niño
Should El Niño develop, it is projected to have notable effects on global weather.
Read More: What Happened in the [Insert Event Name Here] Incident?
Drought and Flooding: El Niño can bring drought to some regions while causing increased rainfall and flooding in others.
Temperature Records: There is a risk that El Niño could contribute to breaking global temperature records, further exacerbating the impacts of climate change.
Agricultural Strain: Changes in precipitation and temperature patterns can significantly affect food production worldwide.
Hurricane Season: El Niño can have an impact on the intensity and frequency of hurricane seasons, though these effects are not always predictable.
Expert Observations and Forecasts
Climate monitoring centers are actively analyzing the data to anticipate the ENSO's future state.
"La Niña is expected to fade away in the weeks ahead, ending a pattern that’s mildly influenced global weather conditions since last autumn." - The Weather Network
"The Oceanic Niño Index (ONI) is NOAA's primary tool to monitor and forecast La Niña and El Niño." - Drought.gov
"Neither El Niño nor La Niña are observed or expected in coming 6 months." - Climate.gov (as of early June 2024)
Outlook and Implications
The transition from La Niña to neutral conditions, with the possibility of El Niño developing later in the summer, presents a complex meteorological scenario.
Read More: New Zealand Storms Cause Damage, Power Cuts, and Deaths
Summer Transition: While El Niño and La Niña tend to have less pronounced impacts during the Northern Hemisphere's summer, their development can set the stage for more significant weather events in the subsequent seasons.
Uncertainty in Prediction: Experts acknowledge that the exact timing and intensity of El Niño's influence can be variable, and its effects are not always guaranteed.
Climate Change Context: The interaction of ENSO cycles with ongoing climate change is a subject of ongoing scientific inquiry, potentially altering how these phenomena manifest and are measured.
Sources
The Weather Network: https://www.theweathernetwork.com/en/news/weather/forecasts/la-nina-is-weakening-el-nino-possible-later-this-year
Summary provided context on La Niña fading and potential El Niño development.
Drought.gov: https://www.drought.gov/news/el-nino-southern-oscillation-and-drought-outlook-united-states-2025-09-08
Summary explained ENSO measurement and its impact on drought in the US.
Politico EU: https://www.politico.eu/article/el-nino-back-flood-cyclone-drought-wildfire-climate/
Summary indicated an El Niño event underway in June 2023 and its potential global risks.
weather.gov: https://www.weather.gov/fwd/enso
Summary provided information on ENSO updates and diagnostic discussions.
CNN: https://www.cnn.com/2024/06/13/weather/el-nino-la-nina-summer-forecast-climate
Summary stated El Niño had ended and La Niña was preparing to take over.
Climate.gov: https://www.climate.gov/enso
Summary confirmed La Niña had ended and the tropical Pacific was in a neutral state.
Read More: Strange Data Changes in Money Markets Being Looked Into






