A Shifting Climate Landscape
China's efforts to address climate change present a complex picture. While a notable decrease in greenhouse gas emissions has been observed for the first time, driven by a significant expansion of clean energy, this is happening alongside a policy emphasis on adapting to a warming world. The vast scale of China's emissions means its actions have a profound global impact, making its approach to climate change a critical factor in worldwide efforts to limit global warming. The challenge lies in understanding whether this emissions dip is a lasting trend or a temporary effect, especially as fossil fuels continue to form the backbone of its energy supply.
China's Climate Policy: A Dual Approach
China's climate strategy appears to encompass two main streams: reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preparing for the unavoidable impacts of a changing climate.
Read More: Plan to Build Big Ice Wall to Save Doomsday Glacier
Emissions Reduction Efforts:
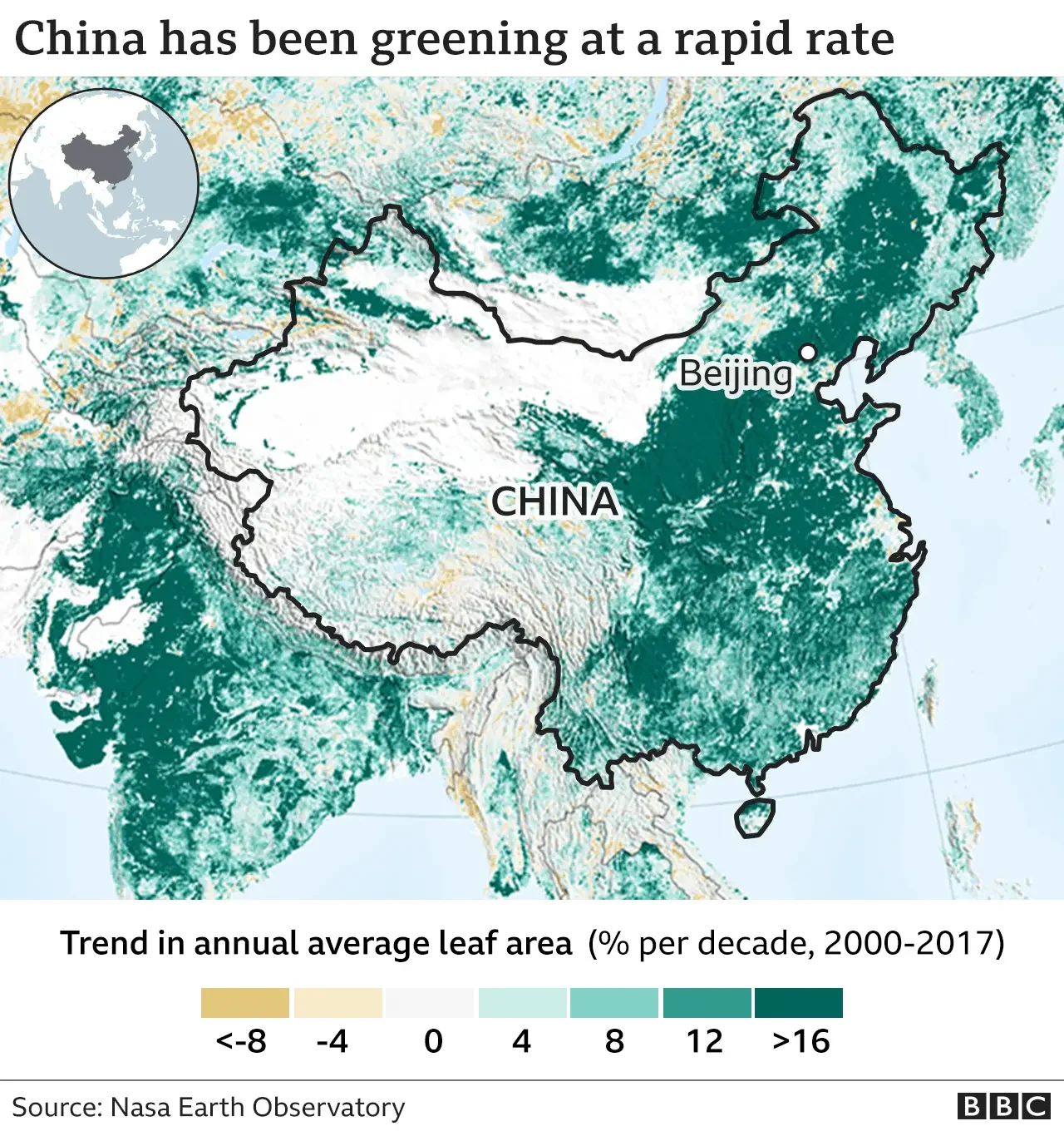
China has become a global leader in renewable energy technology and deployment over the last 15 years.
Renewable energy installations are setting new global records annually.
Nuclear power is being supported as a low-carbon energy source, intended to ensure energy security.
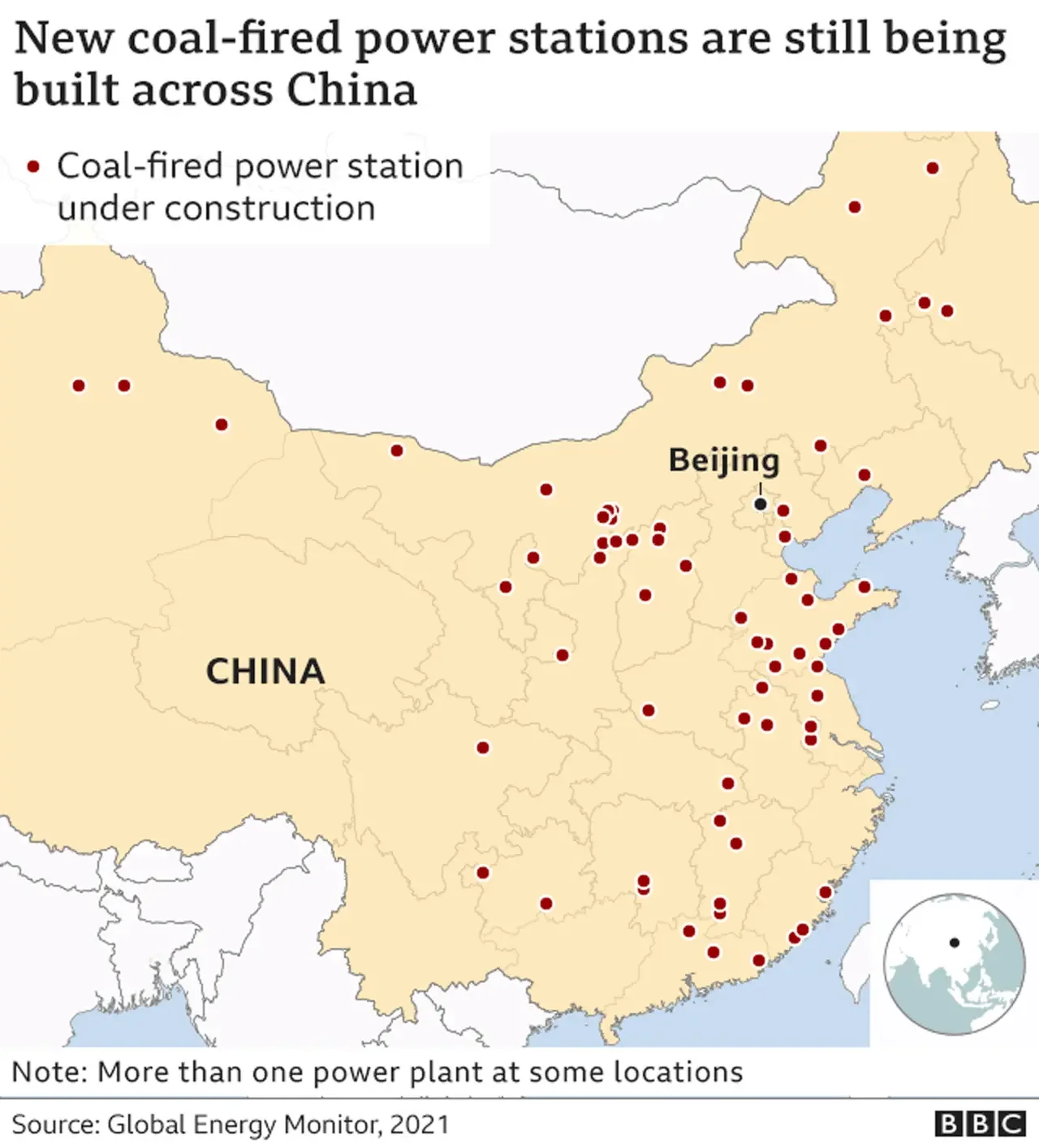
A foundational energy sector law has been enacted, though it does not set specific emission reduction targets.
The law does, however, introduce definitions for energy-efficient buildings, such as "ultra-low energy buildings" and "zero energy buildings."
Adaptation to Climate Change:
A central part of China's strategy involves adapting to rising global temperatures, even with mitigation efforts.
This focus stems from the assessment that global temperatures are likely to exceed the 1.5 degrees Celsius target outlined in the Paris Agreement.
The country faces significant water scarcity in its northern regions.
Evidence of Emissions Decline and Renewable Growth
Recent data suggests a shift in China's emissions trajectory, though the long-term implications are still being evaluated.
Read More: Vietnam and China Clash at Sea Over Patrol Incident

Falling Emissions: For the first time, China's greenhouse gas emissions have decreased. This marks a potential milestone, as previous reductions were linked to economic downturns rather than policy-driven clean energy shifts.
Renewable Energy Leadership: China has invested heavily in renewable energy sources.
It is recognized as a global leader in clean energy technologies.
Annual renewable energy deployment consistently breaks global records.
Fossil Fuel Reliance: Despite advancements in renewables, fossil fuels remain a dominant part of China's energy mix.
The Global Significance of China's Climate Actions
China's role in global climate change mitigation is undeniable due to the sheer volume of its emissions.

Vast Emissions: China's carbon emissions are substantial, significantly larger than those of many other nations.
Global Dependence: Experts agree that substantial reductions in China's emissions are necessary for the world to succeed in its fight against climate change.
Growth Challenges: While all countries face difficulties in reducing emissions, China's economic scale presents unique and significant challenges.
Expert Perspectives and Policy Interpretations
Analysis of China's climate policies highlights differing interpretations and focuses.
Read More: Cartoonist Rohan Chakravarty Uses Funny Pictures to Teach About Nature
Mitigation vs. Adaptation Focus:
Western media often emphasizes China's role in mitigation (reducing emissions) as a critical component of the global climate challenge, often viewing the US and China as the two most important players in this regard.
However, China's domestic approach appears to prioritize adaptation—preparing for the impacts of climate change—over its mitigation efforts. This is based on an acknowledgment that global warming may surpass agreed-upon targets regardless of its actions.
Energy Transition Drivers:
The significant increase in clean energy deployment is presented as a primary driver for the observed drop in emissions.
Nuclear power is seen as a key element in China's low-carbon energy strategy, addressing both emissions concerns and energy security.
Conclusion: A Pivotal Moment
China's climate policies are at a critical juncture. The recent decline in emissions, attributed to a surge in clean energy, is a positive development that could signal a turning point. However, the continued reliance on fossil fuels and the strong emphasis on adaptation suggest that the path to sustained emissions reductions remains challenging. The world's ability to meet its climate goals is intrinsically linked to China's ongoing efforts and the balance it strikes between mitigation and adaptation. Further observation is required to determine if the current downward trend in emissions is sustainable and will be sufficient to contribute meaningfully to global climate targets.
Sources Used
World Economic Forum: Reports on China's clean energy transition and its impact on emissions.
Global energy transition: Tracking China's falling emissions
Climate Action Tracker: Provides details on China's policies and actions concerning climate change.
Brookings Institution: Offers analysis of China's climate priorities, noting a focus on adaptation.
BBC News: Discusses the global importance of China's climate policies.









