The fundamental question of what existed before the Big Bang remains a significant area of scientific investigation. While the Big Bang theory describes the universe's expansion from an extremely hot and dense state, the conditions and nature of any preceding era are not definitively established. Current scientific thought explores various hypotheses, including cyclical universes, the aftermath of previous cosmic events, or an absence of time and space as we understand them.
The concept of the Big Bang has been a cornerstone of cosmology for nearly a century, following initial observations of an expanding universe. However, the idea of a singular starting point, a "singularity," is now often viewed with less certainty by physicists. Instead, the focus has shifted towards understanding the processes that may have led to the Big Bang.
Read More: AI Finds Sperm, Skin Cells Made Into Eggs for Fertility Help
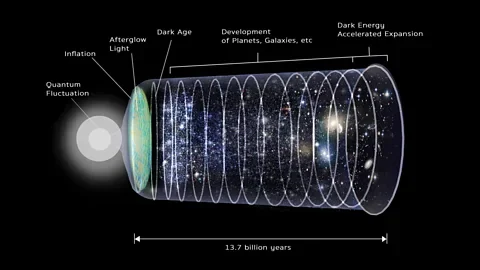
Theories of cosmic inflation, a period of rapid expansion immediately after the Big Bang, are considered by many to be a precursor to the hot Big Bang itself.
Evidence such as temperature imperfections in the cosmic microwave background, the afterglow of the Big Bang, are examined for clues that might differentiate between models with and without a pre-inflationary period.
Some hypotheses propose that the Big Bang was not a singular event but part of a cycle of expansion and contraction, known as a "Big Bounce."
The possibility of a multiverse, where our universe is one of many, is also explored, suggesting the Big Bang could be a rebirth or a quantum event arising from "almost nothing."
Supercomputer simulations are being employed to tackle complex equations that describe extreme cosmic environments, potentially offering insights into pre-Big Bang conditions.
Examining the Evidence for Pre-Big Bang States
The search for definitive proof of a pre-Big Bang era is ongoing, with researchers scrutinizing observational data and theoretical models.
Read More: Cosmic Collision Course: Why Galaxies Crash Despite Universe Expansion!
Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB): Anomalies or specific patterns within the CMB could potentially hold signatures of events or structures that existed before the Big Bang. If signals are found on scales larger than could have been influenced by inflation after the Big Bang, it might suggest an earlier origin.
Inflationary Theory: The prevailing theory of cosmic inflation posits a period of exponential expansion. Many scientists consider inflation to be a pre-Big Bang scenario. Testing predictions of inflation helps refine our understanding of the earliest moments.
Big Bounce Hypothesis: This theory suggests the universe undergoes cycles of expansion and contraction. Evidence for a contracting phase preceding the Big Bang would support this idea. Scientists are developing tests to distinguish between different models of the primordial universe, some of which involve contraction.
Quantum Multiverse: The idea that our universe is a product of a quantum event within a larger multiverse suggests that the Big Bang may arise from a state of near-nothingness.
Competing Theoretical Frameworks
Multiple scientific hypotheses attempt to address the question of what preceded the Big Bang. These frameworks often diverge in their fundamental assumptions and predictions.
Read More: New Ways to Help People Have Babies Using Science

The Role of Inflation
Many physicists now view cosmic inflation as a necessary prelude to the hot Big Bang.
Pre-Big Bang Scenario: Inflation is understood as a phase that occurred before the hot Big Bang, dramatically expanding the universe.
Resolving Mysteries: Inflation is credited with explaining key features of the observable universe, such as its uniformity and flatness.
Testing Inflation: New methods are being developed to rigorously test the theory of inflation and its predictions.
Cyclical Universe Models
The "Big Bounce" theory offers an alternative to a singular beginning.

Expansion and Contraction: This model proposes that the universe contracts, reaches a minimum size, and then bounces back into an expansion phase, effectively creating a new Big Bang.
Continuous Process: In this view, the Big Bang is not a unique event but part of an ongoing cosmic cycle.
Resolving the Origin: The Big Bounce theory attempts to explain both the origin and potential future end of our universe.
Absence of Time and Space
Some hypotheses suggest a fundamental break with our current understanding of causality.
Read More: Drinking Coffee and Tea May Lower Risk of Dementia
No Preceding Time: One view posits that time and space as we know them did not exist before the Big Bang.
A Novel Beginning: The Big Bang, in this context, marks the emergence of spacetime itself, rather than an event within pre-existing spacetime.
Unknowable Past: If time itself began with the Big Bang, the concept of a "before" becomes problematic and perhaps unknowable.
Expert Analysis and Future Directions
Scientific consensus on the pre-Big Bang era is not yet established, with ongoing research and debate shaping current understanding.
"My understanding is that nothing comes from nothing. It is still a physical universe, however empty. Our Big Bang might be the rebirth of one single quantum multiverse, containing infinitely many different universes all occurring together. In this view, the Big Bang arises from an almost nothing." - Article 1 (BBC Future)
"If we can search the Universe for signals that appear on super-horizon scales, that’s a great way to discriminate between a non-inflationary Universe that began with a singular hot Big Bang (which shouldn’t have them at all) and an inflationary Universe that possessed an inflationary period prior to the start of the hot Big Bang (which should possess these super-horizon fluctuations)." - Article 2 (Big Think)
"While the Hot Big Bang is not in doubt, few today take the idea of a Big Bang singularity seriously. In this scenario, what happened before our Big Bang was more inflation, and before that, even more inflation. Therefore, if we use the Hot Big Bang definition (which most physicists believe we should), then inflation must be considered a pre-Big Bang scenario." - Article 3 (BBC Sky at Night Magazine)
Read More: New Way Cells Talk in Tumors Found
Future research aims to refine observational capabilities and theoretical models.
Advanced Simulations: The use of numerical relativity in supercomputers is expected to help solve complex equations related to gravity and the universe's motion, particularly in extreme conditions. This could potentially illuminate scenarios that lie beyond current analytical methods.
Observational Astronomy: Continued observation of the cosmic microwave background and other cosmological phenomena is crucial for finding potential evidence supporting or refuting various pre-Big Bang theories.
Theoretical Refinement: Physicists continue to develop and test models, such as those incorporating dark energy or the properties of axions, to better explain the universe's expansion and origin.
Conclusion
The question of what came before the Big Bang remains a frontier of scientific inquiry. While the Big Bang theory itself is well-supported, the nature of any preceding state is a subject of active research and theoretical exploration.
The theory of cosmic inflation is widely considered to be a key element, describing a rapid expansion before the hot Big Bang.
Observational data, particularly from the cosmic microwave background, are being analyzed for clues that could distinguish between different pre-Big Bang models.
Alternative hypotheses, such as the Big Bounce and multiverse theories, offer compelling explanations but require further validation through empirical evidence and theoretical development.
The limitations of current physics in describing extreme conditions underscore the need for advanced computational tools and continued theoretical innovation.
Sources
BBC Future: What existed before the Big Bang?
Published: January 6, 2022
Link: https://www.bbc.com/future/article/20220105-what-existed-before-the-big-bang
Context: Explores the concept of the Big Bang potentially being a rebirth from a quantum multiverse.
Big Think: The strongest evidence for a Universe before the Big Bang
Published: September 24, 2025
Link: https://bigthink.com/starts-with-a-bang/evidence-universe-before-big-bang/
Context: Discusses the search for super-horizon scale signals in the CMB as evidence for a pre-inflationary period.
BBC Sky at Night Magazine: Cosmologists think we can know what came before the Big Bang
Published: July 25, 2025
Link: https://www.skyatnightmagazine.com/space-science/we-can-know-what-came-before-big-bang
Context: Differentiates between the Hot Big Bang and the Big Bang singularity, framing inflation as a pre-Big Bang scenario.
Harpers: What Came Before the Big Bang?
Published: May 21, 2020 (Original article May 2016)
Link: https://harpers.org/archive/2016/01/what-came-before-the-big-bang/
Context: Presents hypotheses, including the idea that time and space did not exist before the Big Bang.
NASA Science: Overview
Published: September 1, 2020
Context: Provides a general overview of the universe's origin and evolution, noting the historical understanding of its expansion.
BBC Sky at Night Magazine: What came before the Big Bang?
Published: June 9, 2025
Link: https://www.skyatnightmagazine.com/space-science/what-was-before-big-bang
Context: Discusses alternative theories, including a universe with an anti-universe.
BBC Science Focus Magazine: We might finally know what came before the Big Bang
Published: November 4, 2025
Link: https://www.sciencefocus.com/space/big-bounce-expansion-cosmology
Context: Introduces the Big Bounce theory as an explanation for both the beginning and end of the universe.
Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian: What Happened Before the Big Bang?
Published: March 25, 2019
Link: https://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/what-happened-big-bang
Context: Explains that different theories predict different signals and introduces a test for cosmic inflation.
ScienceDaily: What came before the Big Bang? Supercomputers may hold the answer
Published: December 21, 2025
Link: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2025/08/250821094530.htm
Context: Highlights the potential of numerical relativity and supercomputers to model extreme cosmic environments.
University at Buffalo: What came before the Big Bang? UB physicist’s new popular science book explains one leading theory
Published: March 31, 2022
Link: https://www.buffalo.edu/news/releases/2022/03/033.html
Context: Discusses the concept of the observable universe within a potentially infinite space and the role of inflation.
NASA Science: Early Universe
Published: August 22, 2024
Context: Describes the universe immediately after the Big Bang as a hot soup of particles and its subsequent cooling and formation of atoms.
Chennai Astronomy Club Forum: What Came Before Big Bang?
Published: June 17, 2020
Link: https://forum.chennaiastronomyclub.org/t/what-came-before-big-bang/162
Context: Mentions that the trigger for the Big Bang is unknown and discusses cosmological models.
BBC Science Focus Magazine: What was before the Big Bang? Everything you need to know
Published: July 12, 2023
Link: https://www.sciencefocus.com/space/what-was-before-the-big-bang-everything-you-need-to-know
Context: Provides a comprehensive overview of the Big Bang theory and related questions.
Wikipedia: Initial singularity
Published: December 8, 2025
Context: (Content extraction was minimal or failed, therefore this source is not actively used for detailed content beyond its title and existence.)






