A novel engineering feat has created metal tubes that defy sinking, opening doors for more robust maritime applications and new ways to harness ocean power.
Engineers have developed a method to make ordinary metal tubes unsinkable. These specially treated tubes, even when damaged or submerged for extended periods, continue to float. This innovation, stemming from research at the University of Rochester, could lead to safer ships, more stable floating platforms, and methods for generating electricity from ocean waves.
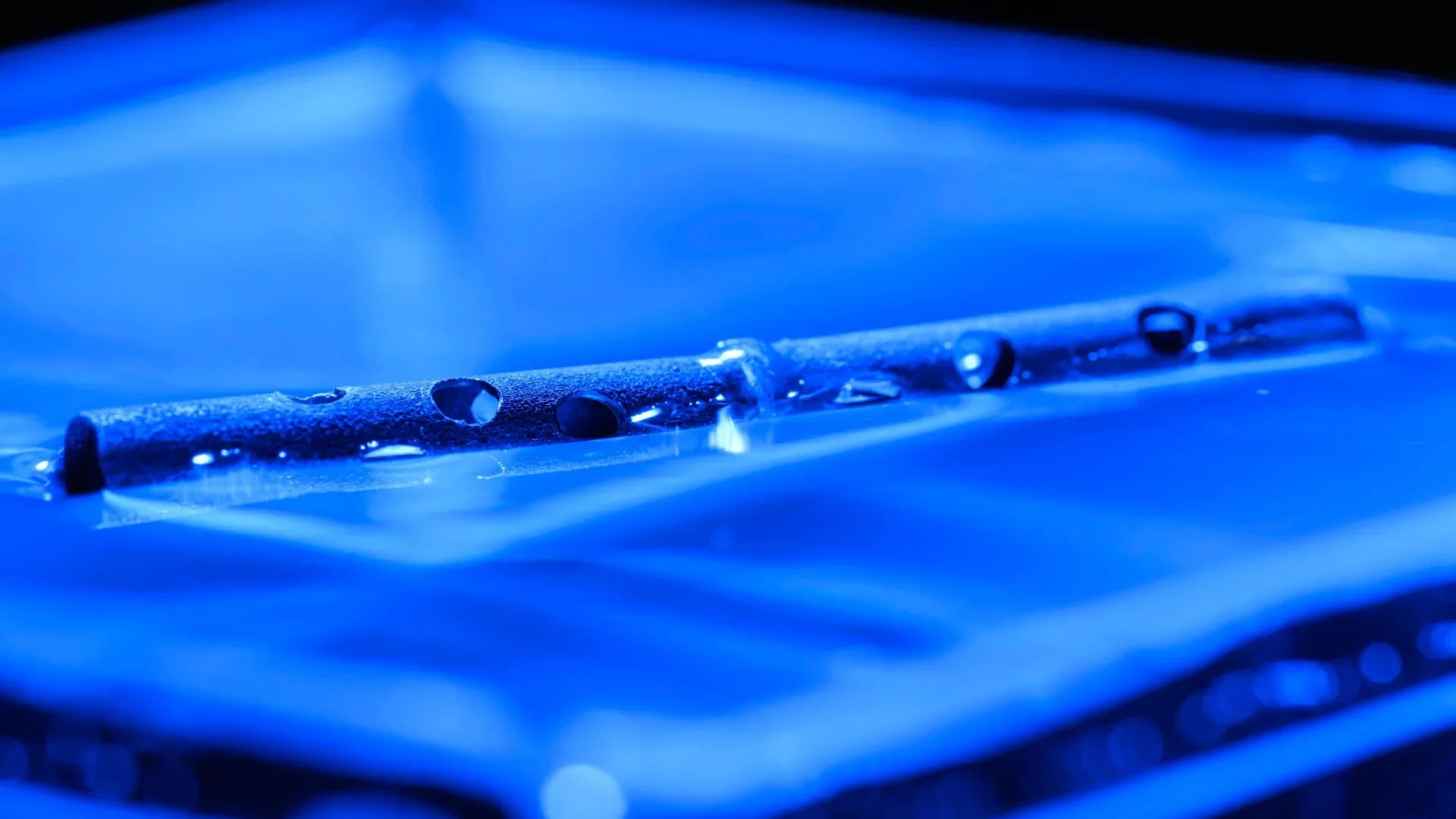

Development of the Unsinkable Tubes
The core of this development lies in a superhydrophobic treatment applied to the metal tubes, primarily aluminum. This surface treatment, combined with a specific internal structure, allows the tubes to trap and retain a stable pocket of air.
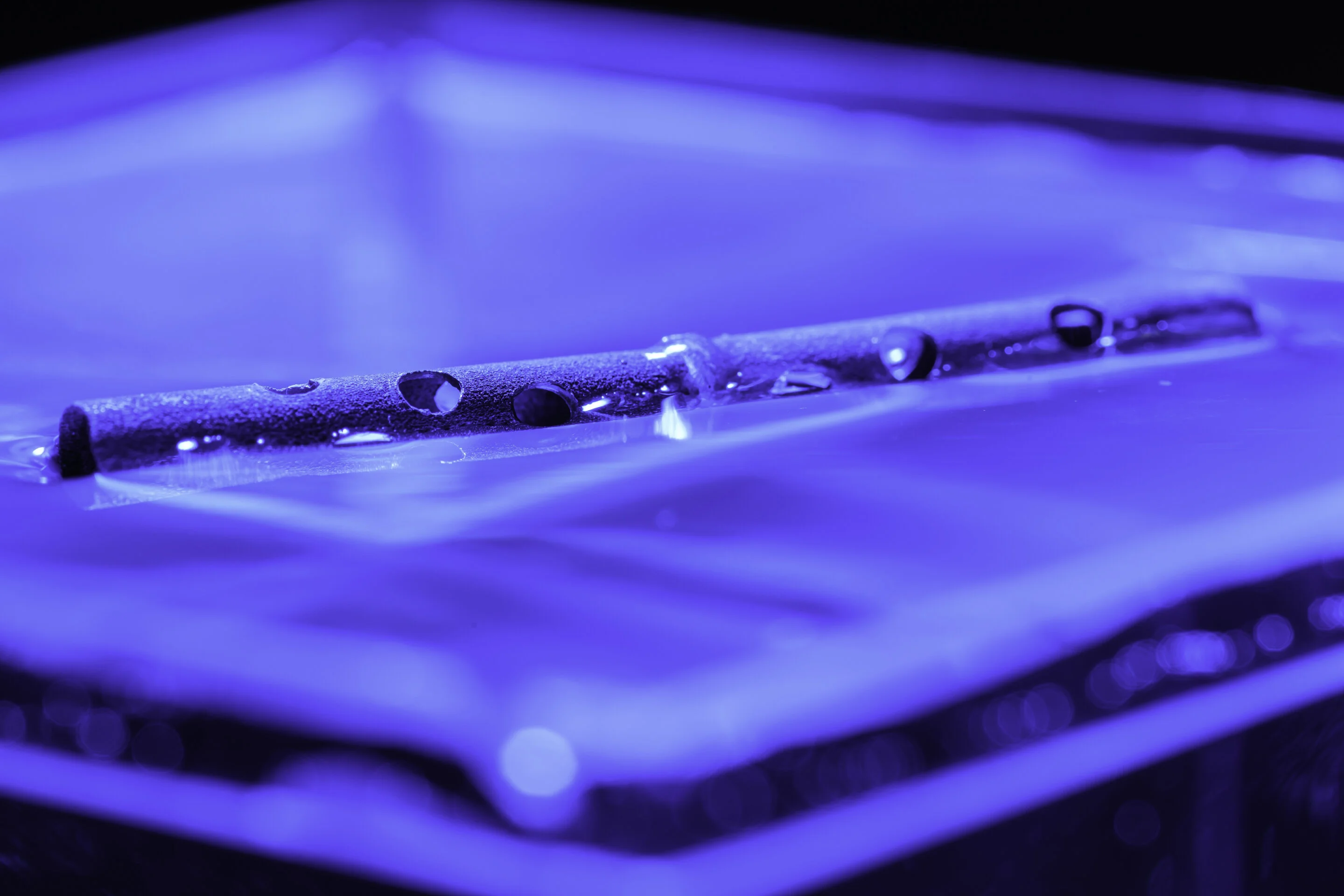
When a treated tube enters water, the superhydrophobic surface repels water.
Crucially, this surface traps air bubbles both inside and around the tube.
This trapped air acts as a natural flotation device, preventing the tube from becoming waterlogged and sinking, even under stress or damage.
Researchers at the University of Rochester's Institute of Optics have detailed this process, with findings published in the journal Advanced Functional Materials.
Demonstrated Resilience and Buoyancy
Tests have shown that these treated tubes exhibit remarkable durability and buoyancy.
Read More: Can New Tech Help Ski Jumpers Fly Farther?
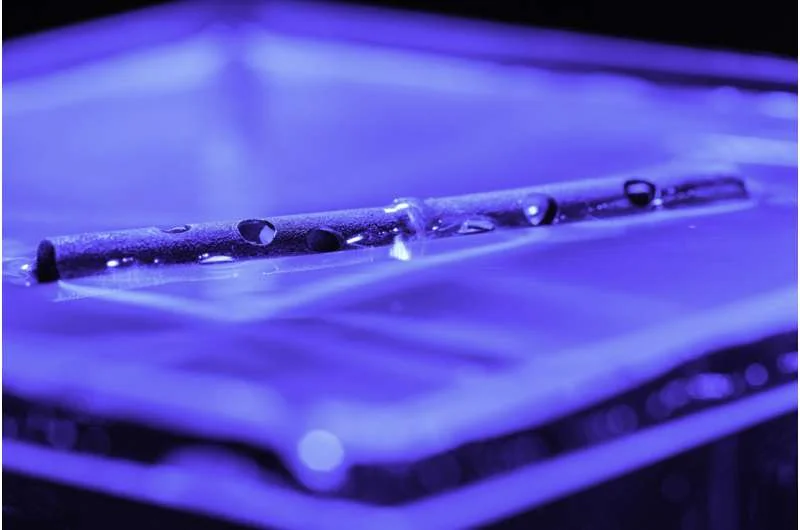
Multiple punctures, cracks, or cuts have not caused the tubes to sink in laboratory settings.
The ability to remain buoyant persists even when subjected to heavy structural damage.
One approach involves adding a divider to the center of each tube to ensure stability from all angles.
Potential Applications
The implications of this technology are far-reaching, spanning maritime safety, infrastructure, and renewable energy.

Maritime Safety: The primary application envisioned is the creation of unsinkable ships or components. This could significantly enhance safety for vessels of all sizes.
Floating Platforms: Linked together, these tubes can form rafts, which could serve as the basis for buoys, floating platforms, and offshore structures.
Renewable Energy: Researchers have demonstrated that rafts constructed from these tubes can be used to harvest energy from ocean waves. This offers a promising avenue for developing new renewable energy systems.
Building Larger Structures
The technology is not limited to individual tubes. The researchers have successfully connected multiple tubes to create larger floating assemblies.
Read More: Experts Say Common Shoelace Knot Is Not Strong
Rafts nearly half a meter long have been constructed by linking treated tubes together.
These larger formations could form the foundation for ships, rafts, and platforms.
Comparison of Key Features
| Feature | Description | Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Superhydrophobic Surface | Repels water, preventing it from adhering to the metal. | Crucial for trapping air and maintaining buoyancy. |
| Trapped Air Pockets | Stable bubbles of air are held inside and around the tube. | Provides the essential flotation force. |
| Damage Resistance | Tubes remain buoyant even when punctured, cracked, or cut. | Enhances reliability and safety in harsh conditions. |
| Modular Design | Multiple tubes can be linked to form larger rafts and structures. | Enables scalable applications from small buoys to large platforms. |
| Wave Energy Capture | Rafts can be configured to generate electricity from moving water. | Opens possibilities for renewable energy generation. |
| Material | Primarily treated aluminum tubes. | Indicates potential for cost-effective manufacturing if scaled. |
Expert Insights
Researchers at the University of Rochester, including Chunlei Guo, a professor of optics and physics, have been instrumental in this development. Their work, published in Advanced Functional Materials, details the process and the scientific principles behind the tubes' buoyancy. The study, titled "Geometry‐Enabled Recoverable Floating Superhydrophobic Metallic Tubes," outlines how the unique surface properties and internal structure work in tandem.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
The development of these unsinkable metal tubes represents a significant engineering advancement. The technology offers a tangible pathway toward creating more resilient maritime vessels, stable floating infrastructure, and innovative renewable energy solutions. The ability of these tubes to withstand substantial damage while maintaining buoyancy is a key factor that distinguishes this innovation. Further research and development could see this technology deployed across a wide range of marine and energy applications.
Sources Used
Scientific American: Unsinkable metal discovery could build safer ships and harvest wave energy
Published: Feb 3, 2026
Link: https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/unsinkable-metal-discovery-could-build-safer-ships-and-harvest-wave-energy/
The Brighter Side: Metal tubes stay afloat even after severe damage — opening the door to unsinkable ships
Published: Feb 6, 2026 (Assuming "2 days ago" from Feb 8th)
Link: https://www.thebrighterside.news/post/metal-tubes-stay-afloat-even-after-severe-damage-opening-the-door-to-unsinkable-ships
University of Rochester: Scientists engineer unsinkable metal tubes
Published: Jan 27, 2026
Link: https://www.rochester.edu/newscenter/unsinkable-metal-tubes-superhydrophobic-surfaces-691642/
USA Herald: US scientists develop unsinkable metal tubes that float even when damaged, offering breakthroughs in maritime safety, offshore platforms, and renewable energy.
Published: Feb 5, 2026
Link: https://usaherald.com/unsinkable-metal-tubes-maritime-innovation/
ScienceDaily: A breakthrough that could make ships nearly unsinkable
Published: Jan 30, 2026
Link: https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2026/01/260130041105.htm
Tech Xplore: Unsinkable metal tubes could lead to resilient ships, floating platforms and renewable energy innovations
Published: Jan 27, 2026
Link: https://techxplore.com/news/2026-01-unsinkable-metal-tubes-resilient-ships.html
The Optimist Daily: Scientists develop unsinkable metal tubes using water-repelling technology
Published: Feb 3, 2026
Link: https://www.optimistdaily.com/2026/02/scientists-develop-unsinkable-metal-tubes-using-water-repelling-technology/
Read More: Talk About Kids and Phones: Like Old Debates About Smoking









