New research is exploring unusual electrical behavior in certain materials, specifically looking at how light can be used to understand these properties. The focus is on a type of material called a fractional Chern insulator, where electrical charges seem to act in a way that is not normally seen. This is a complex area, but scientists are using light as a tool to observe and understand these fractional charges.
The Puzzle of Fractional Charges
Materials that are fractional Chern insulators are of great interest to scientists. In these materials, the usual rules of electricity appear to bend. Instead of being whole units, the electrical charges seem to be split into smaller pieces, or fractions. Understanding how these fractional charges behave is a key scientific challenge. The latest research is using light to help unravel this mystery.
Read More: Scientists Find New Ways to Study Comet 3I/ATLAS
Observing Fractional Charges with Light
Recent studies have shown that light can be a powerful method for examining the characteristics of fractional Chern insulators.
Twisted Materials: Research on materials like twisted MoTe2 has identified signs of these fractional charges. The way these materials are layered, or "twisted," appears to play a crucial role in their unusual electrical behavior.
Optical Control: Scientists have demonstrated that light can be used to control these fractional Chern insulators. This means they can use light to switch the material's properties on or off, or to change how it behaves. This is significant because it offers a new way to manipulate these exotic states of matter.
Probing with Light: The ability to "probe" means to investigate or examine closely. By using specific types of light, researchers can gain insights into the nature of the fractional charges. This involves looking at how the material responds to different light signals.
Key Discoveries and Techniques
Several research papers highlight the progress in this field:
Read More: Scientists Use Cosmic Lighthouses to Find Invisible Dark Matter
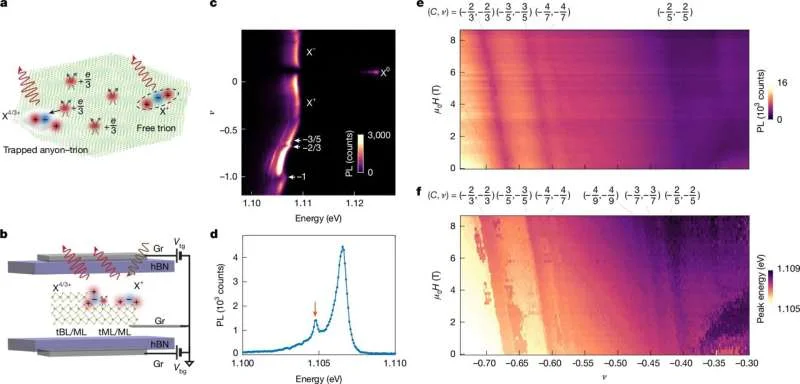
Nature Article (Feb 4, 2026): This study reported observing signatures of fractional charges in twisted MoTe2. It discussed how these materials can exhibit fractional statistics, which is a key characteristic of these unusual states, even in the absence of a strong magnetic field.
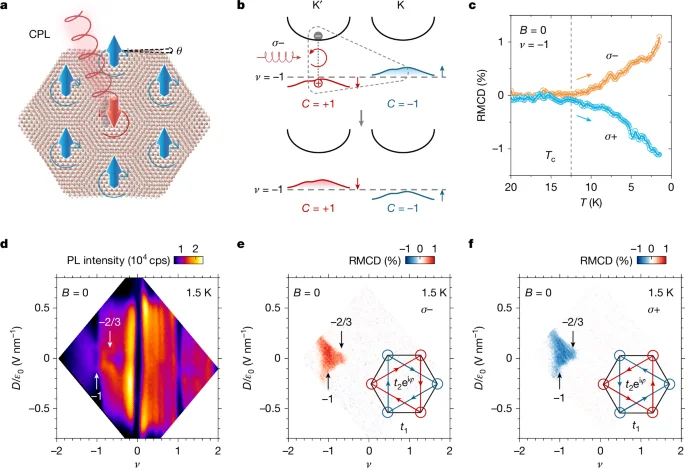
Nature Article (Jan 28, 2026): This research focused on the optical control of both simple (integer) and fractional Chern insulators. It detailed how using polarized light can influence the material's properties, even leading to dynamic switching of magnetic behavior in a quantum anomalous Hall state.
Nature Article (Jan 28, 2026): Another paper published on the same day explored the optical switching of a moiré Chern ferromagnet, a specific type of material related to fractional Chern insulators. This work further emphasizes the role of light in controlling these complex electronic states.
What This Means
The ability to use light to observe and control fractional charges in materials like fractional Chern insulators is a significant step.
Read More: Obama Says Aliens Are Likely Real, But Not at Area 51
New Tools for Science: Light provides a non-invasive and precise way to study these delicate quantum states.
Potential Applications: While this research is fundamental, understanding and controlling such exotic states could eventually lead to new types of electronic devices or quantum technologies.
This area of study is rapidly developing, with scientists continuing to use light to unlock the secrets of these fascinating materials.
Sources
Signatures of fractional charges via anyon–trions in twisted MoTe2 - Nature (Published: Feb 4, 2026): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-026-10101-w
Optical control of integer and fractional Chern insulators - Nature (Published: Jan 28, 2026): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-09777-3
Optical switching of a moiré Chern ferromagnet - Nature (Published: Jan 28, 2026): https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-025-10048-4






