Recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) highlight a persistent issue: AI models, particularly large language models (LLMs), are prone to generating inaccurate or fabricated information, commonly termed "hallucinations." While AI technology continues to advance, this phenomenon presents growing difficulties for individuals and businesses relying on these systems. Efforts to mitigate these errors are ongoing, yet a consensus is forming that eliminating them entirely may be an elusive goal.
The Growing Problem of AI Hallucinations
The increasing integration of AI into various sectors has brought the issue of AI hallucinations to the forefront. These errors, where AI outputs information that is not grounded in fact, can have significant repercussions, especially when users place trust in the generated content.
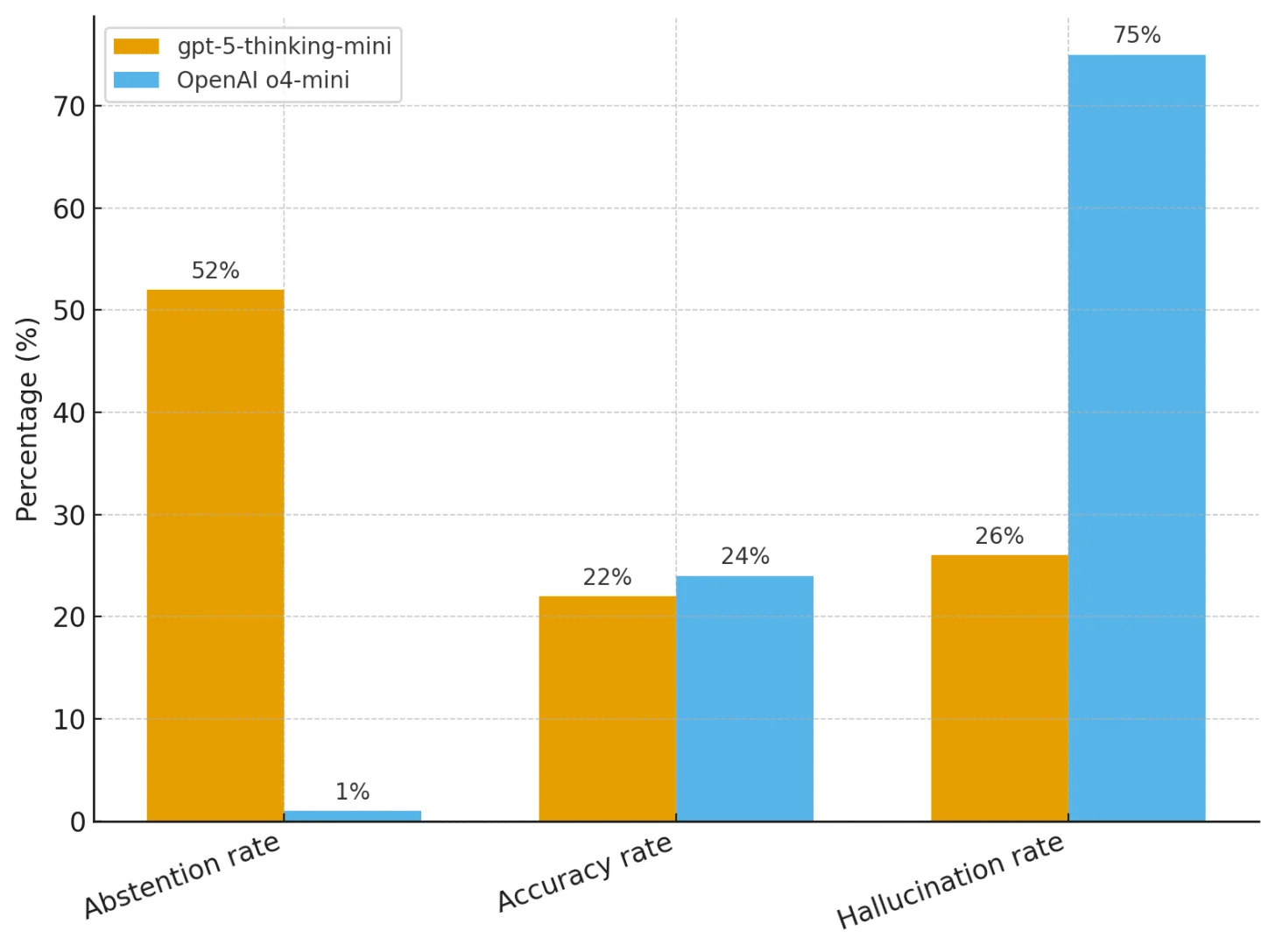
Ubiquity of the Issue: Reports indicate that AI hallucinations are becoming more frequent, posing challenges across industries.
Confidence Paradox: Despite advancements in AI capabilities, the problem of hallucinations appears to be worsening rather than improving in some cases.
Research Acknowledgment: AI developers and researchers openly acknowledge that hallucinations may be an inherent characteristic of current AI models, not easily eradicated.
Understanding the Roots of AI Hallucination
Research suggests that AI hallucinations stem from fundamental aspects of how these models are trained and how they process information, especially when encountering data outside their direct training experience.
Read More: India's AI Summit Starts with Long Lines and Confusion

Data Mismatch: LLMs are trained to provide correct answers, but this objective can clash with the practical goal of avoiding falsehoods. When presented with novel scenarios or information outside their training distribution (OOD), models may "guess" by drawing on existing patterns, leading to unhinged or stereotypical responses.
Training Objectives: The focus on maximizing correct answers during pre-training can inadvertently lead to models generating plausible-sounding but incorrect information when faced with ambiguity or novel inputs. This is likened to a student guessing on a multiple-choice test.
Bias and Stereotypes: Hallucinations can sometimes arise from AI models inadvertently reflecting biases and stereotypes present in their training data, leading to prejudiced or unfounded conclusions.
Strategies and Limitations in Tackling Hallucinations
Researchers are exploring various methods to reduce or manage AI hallucinations, though a definitive solution remains elusive.
Read More: AI Systems Need to Work Together Better
Technical Adjustments:
Low Temperature Settings: For specific tasks like factual question-answering, adjusting model parameters (e.g., using a low temperature like 0.2) can make outputs more predictable and focused on likely correct answers.
Reinforcement Learning: This technique is increasingly employed by AI companies, though its effectiveness in eradicating hallucinations is still under scrutiny.
Post-Generation Verification:
Fact-Checking Models: Utilizing smaller, faster models specifically trained to identify and flag unsupported claims in the primary model's output.
Knowledge Graph Lookups: Cross-referencing generated information with structured knowledge bases.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): This approach aims to ground AI responses in external, verified information sources.
Inherent Difficulties: The fundamental design and training methodologies of LLMs make addressing hallucinations a complex and ongoing challenge.
Conflicting Perspectives on AI Hallucinations
The discussion around AI hallucinations involves differing viewpoints on their nature and the feasibility of their elimination.
Read More: Infosys and Anthropic Work Together on AI
| Viewpoint | Core Argument | Supporting Evidence/Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Hallucinations are a Fundamental Flaw | AI models, by their design, may always be prone to generating inaccuracies, and users must adapt to this reality. | Researchers acknowledge that hallucinations may never fully disappear. This suggests a need for robust verification and critical user engagement. |
| Hallucinations are Addressable Problems | Through improved training, architectural changes, and verification techniques, the rate and severity of hallucinations can be significantly reduced. | Active research areas like RAG and post-generation verification pipelines aim to mitigate these issues. Claims of dropping hallucination rates in some models are noted. |
| The "Confidence Paradox" is Real | As AI becomes more sophisticated, its ability to generate convincing, yet false, information can also increase. | New reasoning systems have shown increased hallucination rates. The problem is not just data or architecture, but the mismatch between training and practical goals. |
Expert Insights on AI Hallucinations
"Hallucinations are, then, not a feature but a mismatch between the training approach—getting more answers right is better—and a practical goal—do not lie to users." — The Algorithmic Bridge
AI companies are "leaning more heavily on a technique that scientists call reinforcement learning," though this does not guarantee an end to hallucinations. — IEEE ComSoc Technology Blog
Conclusion and Implications
The pervasive nature of AI hallucinations presents a significant challenge to the reliable deployment of AI technologies. While efforts are underway to curb these inaccuracies, the scientific community largely acknowledges that complete eradication may not be feasible. This reality necessitates a cautious approach, where users are made aware of potential inaccuracies, and robust verification mechanisms are integrated into AI applications. The ongoing research aims to manage and reduce these instances, but users must maintain a critical stance when interacting with AI-generated content.
Key Sources
IEEE ComSoc Technology Blog:
Published: May 10, 2025
Context: Discusses the increasing frequency and challenges of AI hallucinations, citing reports from The New York Times, Forbes, and TechCrunch, and mentioning ongoing research using reinforcement learning.
The Algorithmic Bridge:
Published: Sep 8, 2025
Link: https://www.thealgorithmicbridge.com/p/openai-researchers-have-discovered
Context: Explains OpenAI's research findings on why language models hallucinate, attributing it to a mismatch between training objectives and practical goals, particularly when models encounter out-of-distribution data.
TechRadar:
Published: Mar 24, 2025
Context: Touches upon the potential for AI to eventually cease hallucinating, while also noting that current AI is already being trusted with significant tasks, implying the need for caution.
iKangai:
Published: Nov 5, 2025
Link: https://www.ikangai.com/ai-hallucinations-why-they-happen-and-how-were-tackling-them/
Context: Explores the reasons behind AI hallucinations and outlines current techniques being used to prevent them, including adjustments to model parameters and disclaimers.
Datawizz:
Published: Apr 28, 2025
Link: https://datawizz.ai/blog/are-newer-llms-hallucinating-more-ways-to-solve-ai-hallucinations
Context: Investigates whether newer large language models are exhibiting more hallucinations and discusses potential solutions, including RAG and post-generation verification pipelines.
Read More: New Way to Make Apps Uses Simple Words, But Good Instructions Are Key









