A urinary tract infection (UTI) can rapidly escalate into sepsis, a life-threatening condition where the body's response to infection harms its own tissues. What begins as a localized infection can, within hours, lead to a systemic crisis requiring immediate medical intervention. The swiftness of this progression underscores the urgency of recognizing and addressing UTI symptoms promptly.

The Grim Trajectory: From UTI to Sepsis
Urinary tract infections are common, particularly among women. While often manageable with antibiotics, a failure to treat or a delayed diagnosis can allow the infection to spread. This unchecked spread can trigger urosepsis, a specific type of sepsis originating in the urinary tract. Evidence suggests that in some instances, the transition from a mild UTI to severe sepsis is alarmingly rapid, transforming a treatable ailment into a dire medical emergency.
Read More: New Papers Show Epstein Had Health Problems with Sex Hormones

A UTI is an infection within the urinary tract.
Urosepsis occurs when an untreated UTI spreads to the kidneys and leads to sepsis.
Recognizing the Signals: Symptoms of Sepsis
Identifying sepsis hinges on recognizing a combination of symptoms, which can vary greatly among individuals. A key indicator is the presence of an infection, often accompanied by a fever as the body attempts to combat the invading pathogens. However, atypical presentations are not uncommon, especially in vulnerable populations like the elderly, who may not exhibit the classic signs of infection.
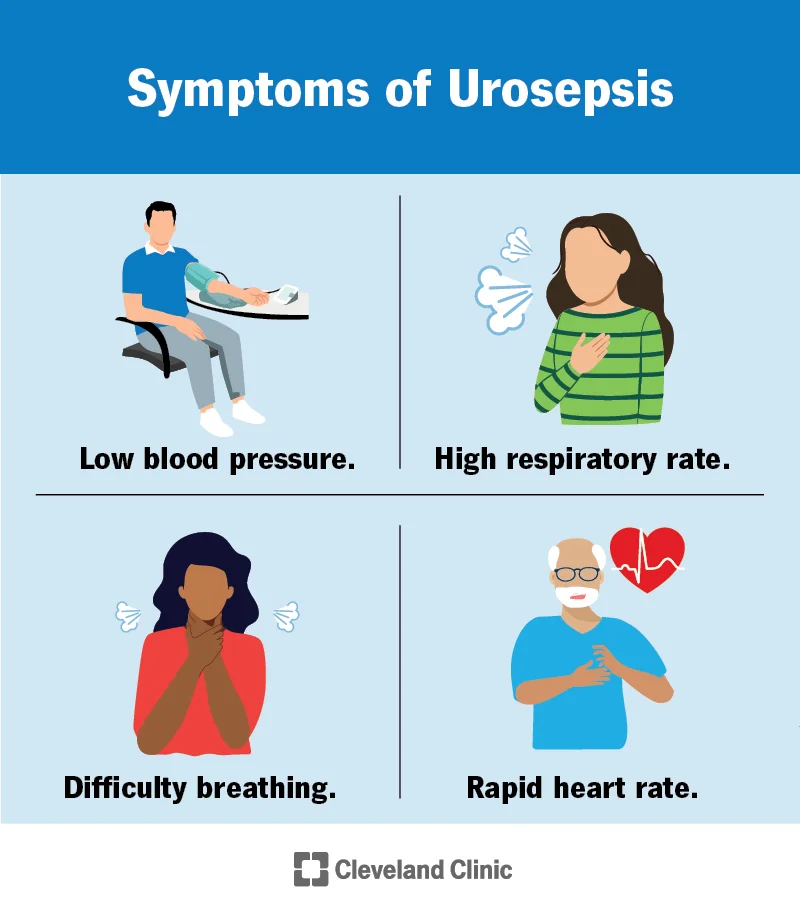
Infection: Signs and symptoms of an infection may be present.
Changes in mental status.
Fever.
Fatigue.
Pain.
Elderly individuals may present with unusual symptoms or none at all.
The Rapid Onset of Crisis
Anecdotal accounts highlight the precipitous nature of sepsis development following a UTI. In some reported cases, individuals experienced vomiting and a swift decline in health, necessitating hospitalization and intensive care within a matter of hours. This rapid deterioration can result in prolonged recovery periods, encompassing both physical and psychological challenges. The severity can even lead to septic shock, a critical condition where blood pressure drops dangerously low and organs begin to fail.
Read More: Actor James Van Der Beek Dies at 48 from Bowel Cancer; Early Signs Often Missed
Rosie was hospitalized for four days after her UTI escalated to sepsis.
Ms. Carson went into septic shock hours after her symptoms failed to improve, requiring urgent surgery.
The Urgency of Medical Attention
The rapid progression of sepsis necessitates prompt medical evaluation. When UTI symptoms persist or worsen, or when new, concerning signs emerge, seeking immediate professional medical advice is crucial. This proactive approach can be pivotal in preventing the infection from advancing to sepsis or its more severe forms. Public health bodies and advocacy groups stress the importance of "Just Asking: Could it be Sepsis?" when symptoms are concerning, encouraging timely calls to emergency services or visits to emergency departments.
Contacting a doctor immediately upon suspecting a UTI is advised to prevent urosepsis.
If a UTI is confirmed and sepsis is suspected, immediate medical care is paramount.
Expert Perspectives on Sepsis and UTIs
Medical professionals emphasize that while infections are the primary trigger for sepsis, the body's reaction can be the harmful element. This can involve an overwhelming immune response to the infection or, conversely, an overreaction by the immune system. There is currently no definitive method for preventing sepsis entirely. However, minimizing the risk of serious infections, such as UTIs, is seen as a strategy to reduce the overall chance of developing sepsis.
Read More: Know the Early Signs of Colon Cancer
Sepsis arises when the body's immune system overreacts to an infection or a toxic substance.
Reducing the incidence of severe infections can lower the risk of developing sepsis.
Conclusion: Vigilance and Swift Action
The link between urinary tract infections and sepsis presents a significant public health concern. The swift and often unpredictable escalation from a common infection to a life-threatening condition underscores the critical need for heightened awareness and prompt medical intervention. Recognizing the diverse symptoms of sepsis and understanding the potential for rapid decline are vital. Prompt medical consultation for persistent or worsening UTI symptoms, and immediate action when sepsis is suspected, remain the most effective strategies to mitigate the severe consequences of this dangerous condition.
Sources
Daily Mail:
I had a UTI, then in hours I was fighting deadly sepsis (Published: 13 hours ago)
Woman given hours to live after UTI complications triggered sepsis (Published: October 13, 2025)
Cleveland Clinic:
Sepsis from UTIs (Published: December 3, 2025)
Sepsis.org:
Symptoms (Published: January 5, 2023)
Harvard Health:
Sepsis symptoms: Recognizing the need for urgent medical care (Published: April 2, 2024)
Sepsis Trust:
About sepsis (Published: September 12, 2025)
WebMD:
What Is Urosepsis? (Published: July 6, 2023)
End Sepsis:
Sepsis from UTI | Understanding the Link for Effective Prevention (Published: August 6, 2025)
Read More: AI Finds Sperm, Skin Cells Made Into Eggs for Fertility Help





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/VWH_EarlySignsofColonCancer-be7dc99d4bfb4a37b2e6bec8d9f4cfd7.png)
